Introduction
Today we’re going to present you a short presentation about the last Nobel Price of Chemistry which was awarded last week on Wednesday.
Actually, this year the price was awarded by 3 researchers: the first half was attributed to a woman, Frances Arnold, and the last part was attributed to two co-workers, Gregory Winter and George Smith for their work on enzyme and protein.
Now we’re gonna try to explain you what their work was and how revolutionary it could be for the future.
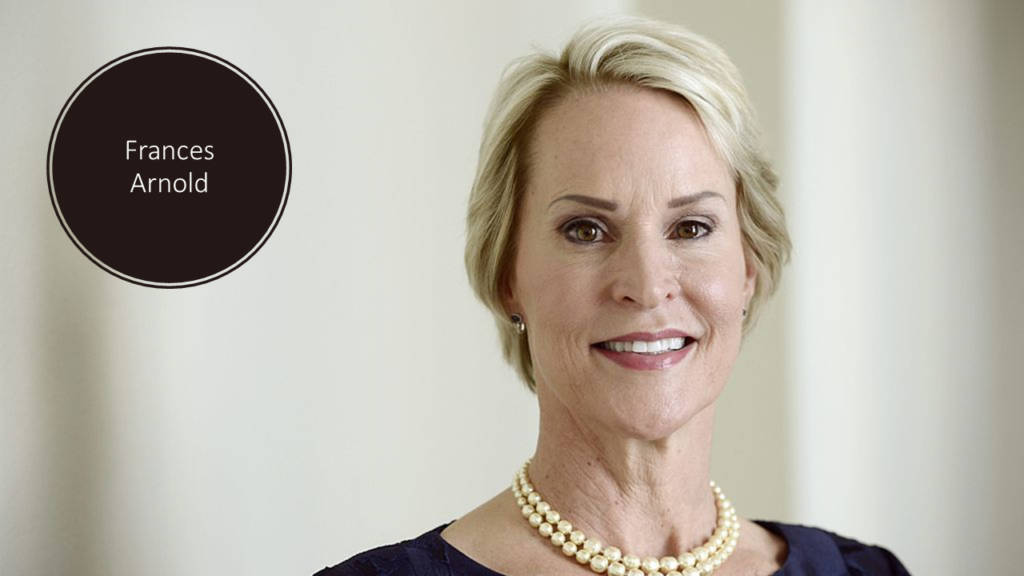

Directed Evolution of enzymes
The first half part was awarded to Frances H. Arnold “for the directed evolution of enzymes”. She is only the fifth woman who won this prestigious price. Frances Arnold is a 62 years old doctor that’s doing her researches in the California Institute of Technology. I’ll give you a short summary of her personal life. She had one son that died of cancer in 2001. She later got married and had two sons, and she lost again one son who died in an accident. And after that, she was diagnosed with cancer and underwent treatment for 18 months. I think we could say that she is a warrior woman. Maybe she deserves another Nobel-price for that.
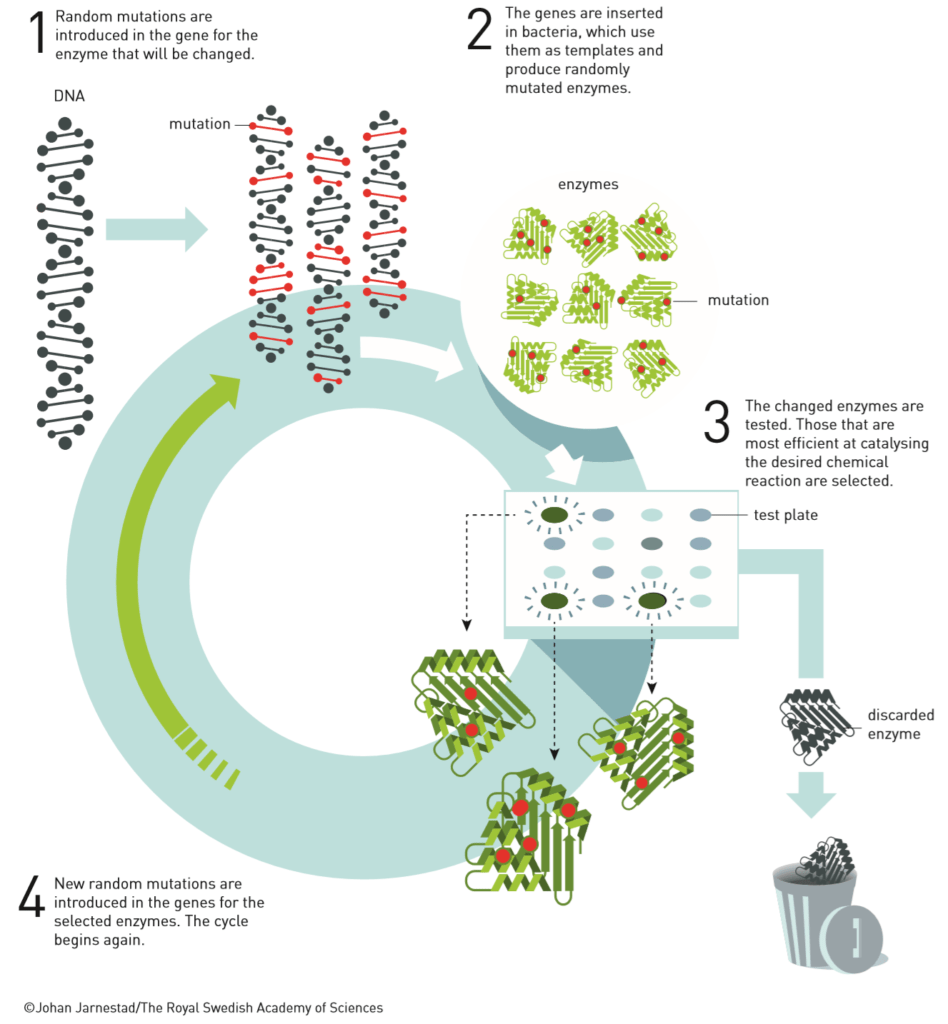
Now, let’s talk about the directed evolution of enzymes. Arnold did her researches in order to improve enzymes catalysis. This is a new way of catalyzing chemical reactions with a more sustainable and greener catalyzer. Which makes them even more interesting, is that enzymes are proteins abundant in the living world. So, she decided to find a way to create the best and more efficient enzymes to catalyze any reaction. She created a sort of protocol/method you should follow.
Here is a representative diagram. =>
You try DNA combinations while keeping the good ones. So, you have more luck to create a more efficient one at each cycle. It’s based on probabilities, but the cycle has its limits.
Thanks to the cycle, you will get even more efficient enzymes. In fact, after a few cycles of directed evolution, an enzyme may be several thousand times more effective. It’s an incredibly strong method.

Enzymes produced through directed evolution are used to manufacture everything from biofuels to pharmaceuticals with a an environmentally friendly way.
Phage display of antibodies
Now we’re going to talk a little bit about the work of Gregory Winter and George Smith. The first is a british biochemist who is 67 years old and who works essentially on antibody and the second one is an american researcher and professor at the university of Missouri in Columbia. His work is mainly dedicated to peptides which are molecules composed of amino acid. A succession of peptides connected between us forms a biologic macromolecule, known under the name of protein.

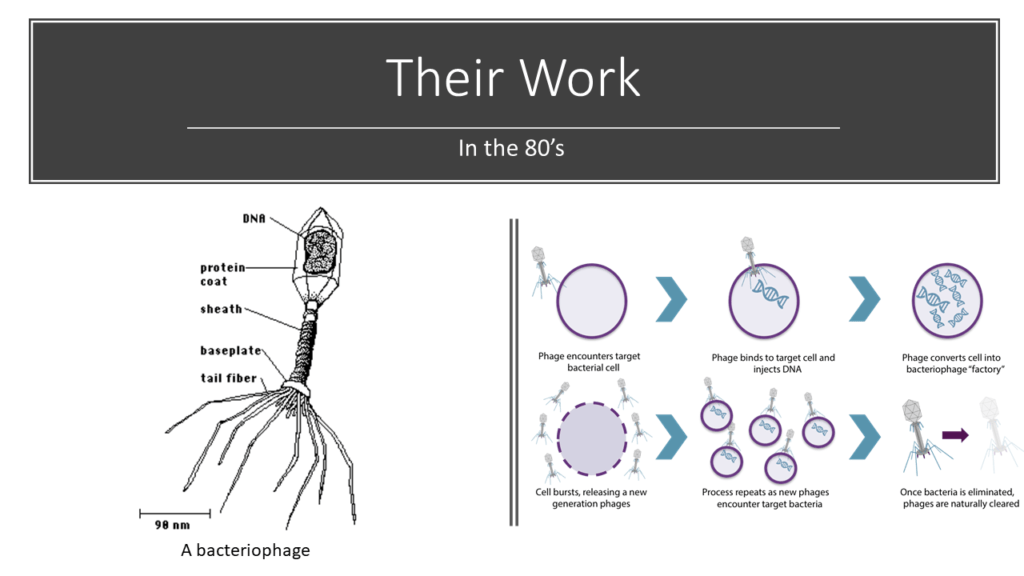
During the 80’s, George Smith was working on bacteriophage which are virus which attack bacteria only delivering them the genetic material they contain in a protective protein, in order to destroy their metabolism. Thus, they reproduce and create new bacteriophages.
One day, he imagined that he could be possible to use those bacteriophages differently. He suggested to introduce a particular gene in the protein coat in order to produce, after the transfer of the genetic material in the bacteria, a new peptide directly introduced in the protein coat of the newborn bacteriophage. This peptide could be, later, be fixed by an antibody.
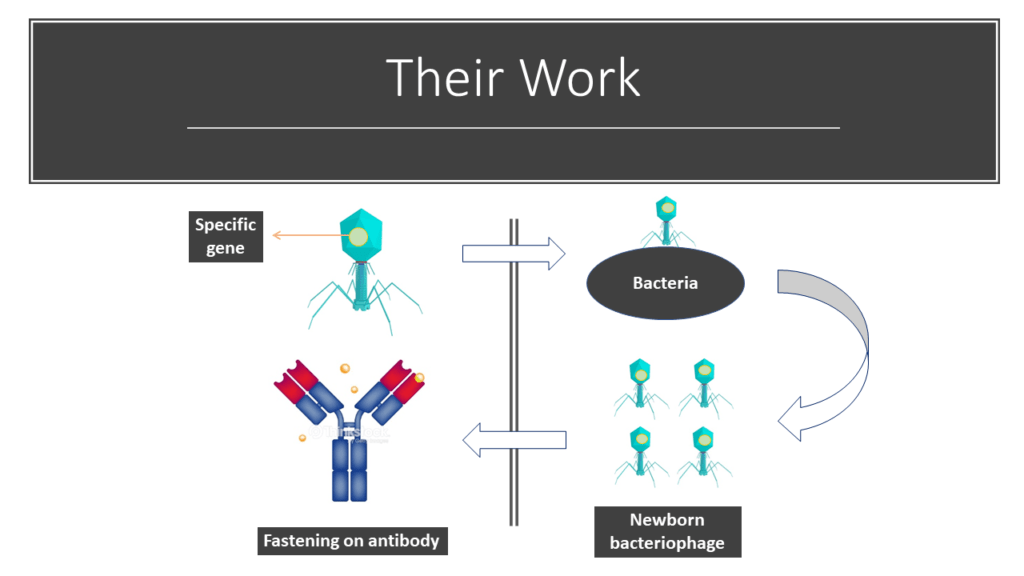
And then, in the 90’s, Gregory Winter decided to use this method to make new biomolecules. He created some bacteriophage which had on the surface of their protein coat the site of fastening of a specific antibody. Thanks to this work, it was possible to attract and extract one specific antibody for a specific use, through millions of other antibodies.

Combining his work with the one of Frances Arnold and her directed evolution method, Gregory Winter applied the method on his antibodies in order to develop new medecines or even the phagotherapy.
As an example, in 2003, a new medicine named “Humira” was created thanks to this method and is used to fight against inflammatories diseases like psoriasis. Other antibodies from this technique are able to neutralize toxins or used to fight against metastasised cancer.

To conclude, we could say that it’s the start of a new era in chemistry. The methods that the 2018 Nobel Laureates in Chemistry have developed are now being internationally developed to promote a greener chemicals industry and improve the image of chemistry around the world. These new methods will produce new materials, will manufacture sustainable biofuels, mitigate disease and save lives. Finally, the directed evolution of enzymes and the phage display of antibodies have brought the greatest benefit to humankind and start a revolution in chemistry.
Sources :
https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemistry/2018/press-release/
https://www.nobelprize.org/uploads/2018/10/popular-chemistryprize2018.pdf
https://www.nobelprize.org/uploads/2018/10/advanced-chemistryprize-2018.pdf
Written by:
- Eddy Barraud
- Marie Augereau